Manage Pending Hosts
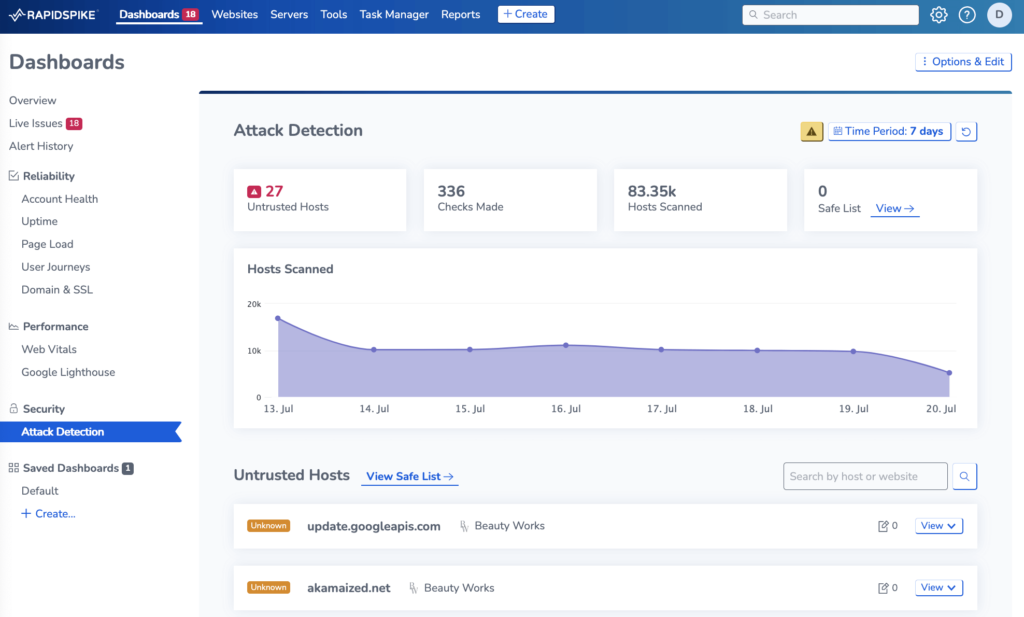
RapidSpike’s Attack Detection monitors data that your website is sending to other destinations. RapidSpike automatically recognizes safe hosts (like Google or Facebook). Pending hosts are destinations that RapidSpike does not recognize. You can see the list of pending hosts on the Attack Detection dashboard.
Where to find Pending Hosts
Go to the Attack Detection page to view a list of your pending hosts.
Trust a host
If you recognise a host marked as ‘pending’, click View > Trust to add the host to your Safe List. This will stop it from appearing as a pending host again.
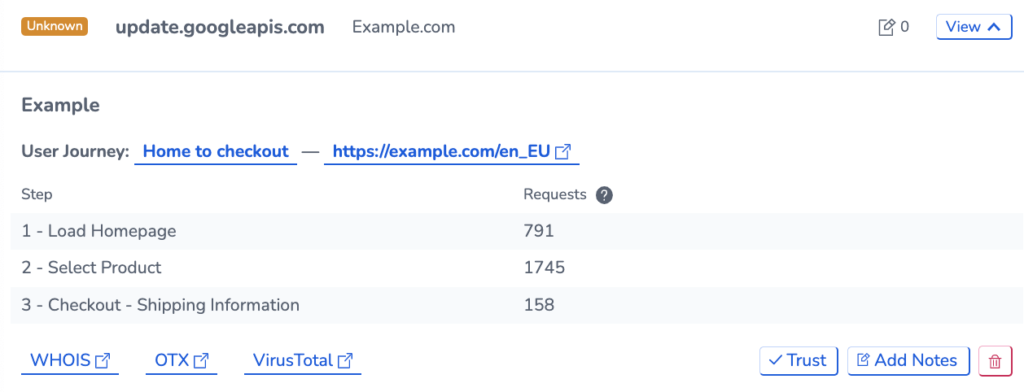
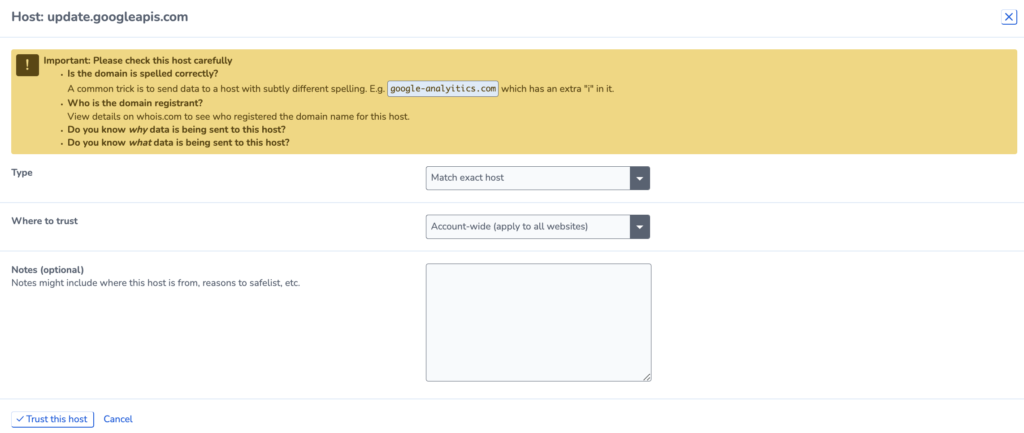
Fill in the options on the following page to trust the host:
- Set the type. This instructs RapidSpike on how to recognise the host. This can be either by the exact URL or following a specified pattern.
- Where to trust: choose between specific websites or account-wide.
- Notes: Add notes about why you are trusting the host. You should identify why and what it is doing on the website.
- Select Trust this Host.
Why has an Pending Host Appeared?
Sometimes, you might not recognise a pending host, or it might not show up in all test results. There are many reasons why this can occur:
- If someone in your marketing team added a plugin to your website and then later removed or edited it (possibly using Google Tag Manager), this might result in a temporary change.
- A/B testing: If you’re conducting A/B testing on your website, this could cause variations in the data
- It’s also possible that a third party briefly redirected or used a new resource on your website due to a spike in traffic volume, a specific time of day, a deployment or code change, or even a routing or configuration error.