Understanding the Magecart Threat
Magecart attacks, also known as web-skimming, formjacking or supply chain attacks, are a client-side attack method used to steal customers’ payment data from websites.
This is the number one threat to e-commerce sites today.

Ensure PCI DSS v4 Compliance
Monitoring scripts is a key part of new PCI DSS v4 requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1, designed to tackle the Magecart threat.
How do these attacks happen?
Hackers usually exploit a vulnerability on a web server, gaining access to either inject malicious JavaScript code or edit the HTML of the website to call a new third-party JavaScript file.
Your website loads third party add-ons
Nearly every website has third party plugins, or tags, used to load additional content or functionality.
Tags might include live chat, customer support, social media, ads, trackers, A/B testing, analytics or many more.
Did you know?
The average e-commerce website has 42 third party add-ons. Some third parties even load other third parties.
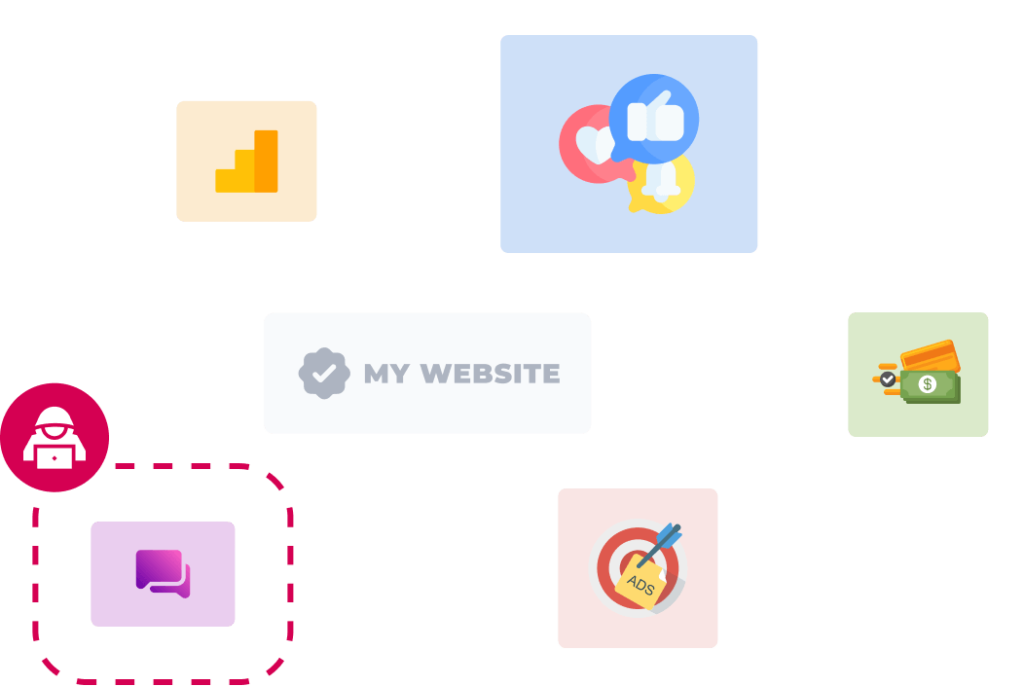
A vulnerability leads to one of your third parties being compromised
Hacking groups target one of your third party add-ons, or your own website directly, and gain access. Add-ons might have been added via Google Tag Manager, via a content management system, or directly. You may not even be aware that hackers have gained access.
Did you know?
Your website is only as secure as your weakest third party.
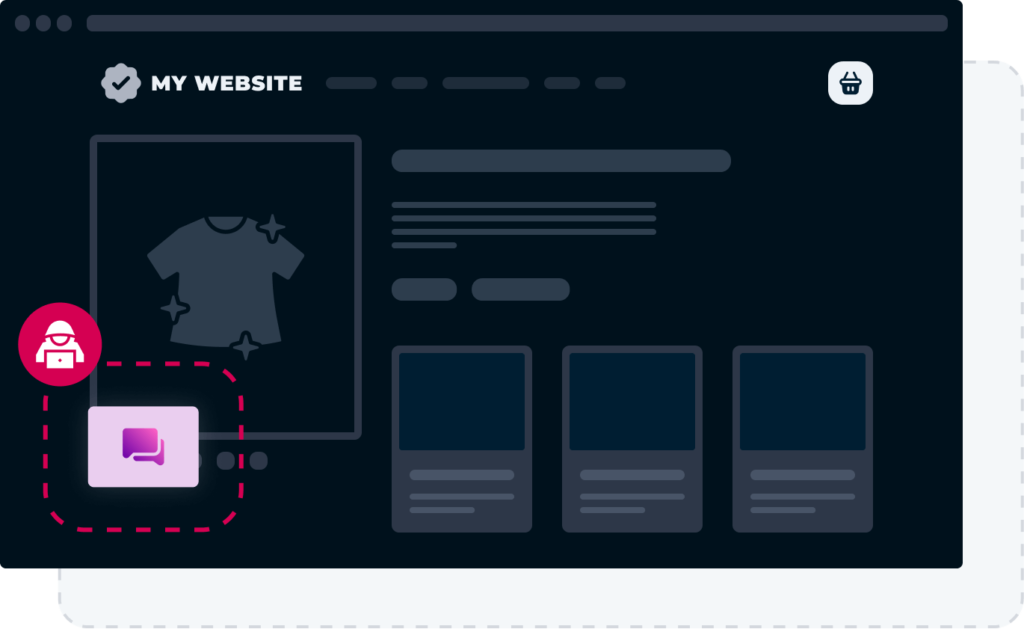
The compromised code is then running on your website
Your website loads code from a compromised third party, which enables hackers to execute Javascript on your customers’ browser.
These attacks are then happening “client-side”, where customer interactions can be monitored or intercepted.
Did you know?
Common methods include “key-logging”, where all user keypresses are recorded and sent to the hackers.
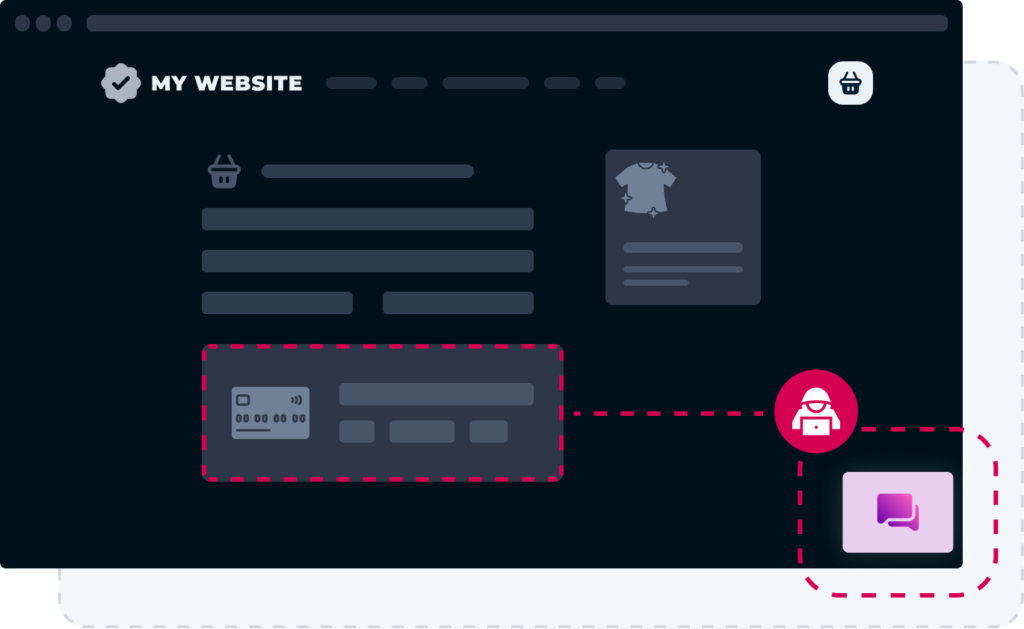
Sensitive data is taken without the user being aware of it
These attacks are usually focused on card payment screens, where the card details are “skimmed” by the Javascript on the website. The transaction will go through as normal, but card details have been copied and sent to a destination under the hacker’s control.
Alternatively, the compromised script loads a fake payment form instead of the secure one, and customers unwittingly enter their details there.
Did you know?
Customers and website owners might not even be aware an attack has occurred.
Other WebSkimming Attack Vectors
Attacking via third parties is not the only route in for client-side attacks to take place. Other methods include:
Web-skimming attacks often include domain spoofing to assist in going undetected. The British Airways malicious skimmer exfiltrated card details to a spoof domain, ‘baways.com’. To an untrained eye, many of these domains could be seen as legitimate.
Steganography-based skimmers hide code within imagery to avoid detection. The Tupperware website was one victim of this style of attack, with malicious code hidden within a PNG file that activated a fraudulent payment form during the checkout process.
Some attacks load a fake checkout
form before the legitimate checkout page or before a PayPal page. A Synthetic User monitor can continuously walk through the checkout page and alert to any new hosts found, potentially before a data breach occurs.
Case Studies – Magecart Attacks
These web-skimming attacks have targeted business both large and small. In the most impactful cases, millions of customers have been affected, with substantial fines levied against the compromised websites.

British Airways
Details were taken via a script designed to steal financial information by skimming the payment page before it was submitted.
£20 million fine
380,000 customers’ details affected
16 days of attack before detection

Ticketmaster
Malicious software on third-party customer support product caused the hack. Stolen details included; names, addresses, email addresses, telephone numbers, and payment details.
4 months before detection
40,000 customers impacted

Volusion
Infected for 26 days before detection.
Volusion are an e-commerce shopping cart provider. The malicious file and domain were both disguised to look legitimate.
6,589 websites affected
239,000 payment details sold for $1.6 million

Vision Direct
JavaScript file was injected into the Vision Direct website posing to be a legitimate Google plugin. Vision Direct have provided all affected customers with an Identity Monitoring Service.
5 days before detection
6,600 customers’ details stolen

Macy’s
The breach occurred from October 7th-15th, 2019. An unauthorised third-party added malicious code to two pages on macys.com, including the checkout page and the wallet page.
1 week before detection

AMCA
AMCA have filed for Chapter 11 protection
and listed assets of $10 million. Multiple
lawsuits have been filed against AMCA.
20 million US citizens affected
$3.8 million spent on mailing individuals
Website compromised for 8 months

Magecart Attack Detection
Need help monitoring for third party script changes? Want to comply with PCI DSS v4?
Get award-winning e-commerce security from CartShark.